15.5.1 Authenticated encryption with CCM
To apply CCM, sender Alice must provide the following four inputs:
- The shared secret key ke.
- A nonce n that must be unique within the scope of ke. (In other words, the set of nonces used with ke must not contain duplicate values.)
- Plaintext message m.
- Additional authenticated data d. (This data is not encrypted and can be used to authenticate plaintext packet headers or contextual information. If Alice has no data d, she can simply input a zero-length string.)
How to perform authenticated encryption with CCM based on these four inputs is illustrated in Figure 15.4.
Alice first applies a formatting function to nonce n, plaintext m, and additional data d to produce a sequence of blocks B0,B1,…,Bn. Alice then computes the authentication tag T using CBC-MAC as shown in Algorithm 3, with M being the size of the authentication tag in bytes. This is shown in the lower half of Figure 15.4.
Algorithm 3: Computation of MAC value T in CCM using CBC-MAC
Require: Sequence of blocks B0,B1,…,Bn, shared secret key k
Ensure: Message authentication tag T
X1 ← ek(B0)
for i = 1 … n do
Xi+1 ← ek(Xi ⊕ Bi)
end for
T ← first M bytes(Xn+1)
return T
In the next step, Alice encrypts the plaintext message using CTR mode. Each input Ai to the block cipher is composed of the following:
- A flags field, containing information about the message length, the length of the authentication tag, and whether there is additional authenticated data or not
- The nonce n
- The counter value ctri
In other words, each 128-bit plaintext block mi is encrypted to a 128-bit ciphertext block ci by XORing it with the block cipher output for the value Ai (essentially, the counter value):
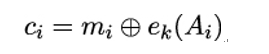
Here, ek is the block cipher’s encryption operation under the shared secret key k.
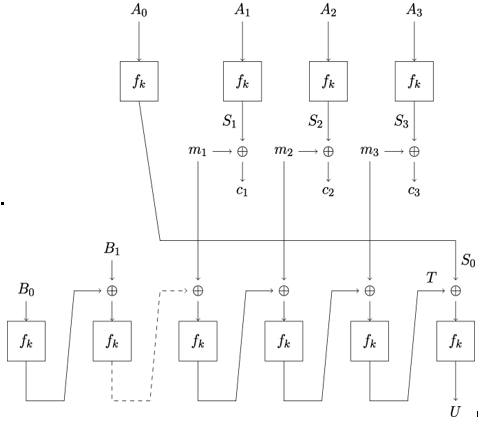
Figure 15.4: Working principle of the CCM mode of operation. The dashed line indicates that a sequence of blocks up to Bn is processed
In the final step, the very first key stream block S0 = ek(A0) is used to encrypt the authentication tag T computed in the first step:
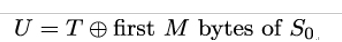
The CCM output consists of the ciphertext c, the concatenation of the ciphertext blocks ci, and the encryption authentication value U.